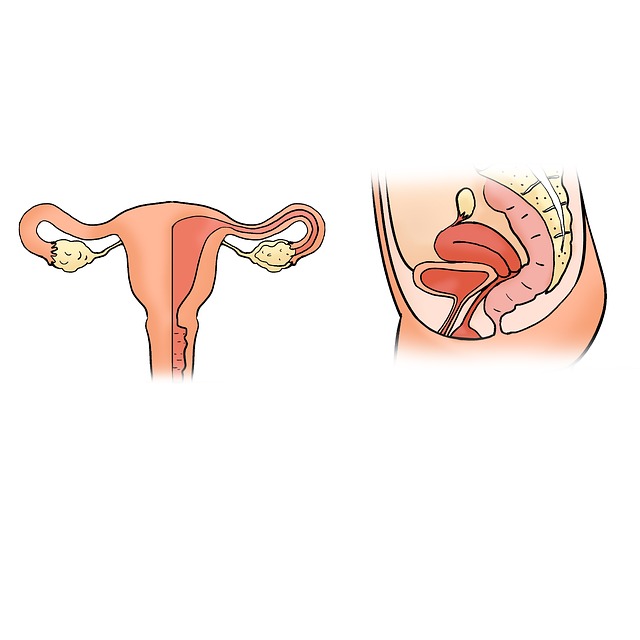
Uterine disorders can impact female fertility. Often uterine problems lead to implantation difficulty or increase the tendency of miscarriage.
Uterine fibroid or myomas can be benign tumors or polyps. Therefore, they are noncancerous outgrowth in the inner wall of the uterus. This type of growth can cause blockage in the fallopian tubes. Blockage of fallopian tubes can interfere with implantation and causes infertility. The exact reason for fibroid is not known. But the genetic reason may be a reason for uterine fibroid.
Almost 5% to 10% of female infertility occurs due to uterine fibroids. However, every woman with uterine fibroid or polyps does not face difficulty in pregnancy, as the size and location of uterine fibroid or polyps responsible. It has been found that the fibroid sited in the uterine cavity with 6 cm in diameter or in larger mainly responsible for female infertility. Uterine fibroid can interfere with female fertility in the following condition:
- Cervix position alteration causes restricted entry of sperm in the uterus.
- Uterus shape alteration due to uterine fibroid formation causes restricted sperm movement within the uterus and prevent implantation.
- Fallopian tube blockage prevents sperm to meet with the egg in the uterus for fertilization. Therefore, it causes infertility.
- Uterine fibroid can interfere with blood circulation within the uterus which prevents embryo implantation.
Apart from uterine fibroid, the following are some uterine disorders that can cause female infertility:
- Uterine inflammatory disorder and endometriosis scarring can interrupt implantation.
- Congenital uterine abnormalities like uterine shape disorder can cause a problem in conceiving or carrying difficulty.
- Cervical stenosis makes the cervix narrow and can damage the cervix due to inherited malformation.
- The cervix is unable to produce lubricative mucus which supports sperm motility into the uterus through the cervix.
Reference:

Ravi Sharma is a self-motivated, successful entrepreneur and has a solid experience in the fertility segment. and he is the director at ARTbaby Global (ARThealthcare). He is a pharmacy graduate with post-graduation in business administration and has 14 years of rich experience in the field of infertility segment. He loves to write about IVF, Surrogacy, and other ART (assisted reproductive technology) news, issues, and updates. He is a Pharmacy graduate (B. Pharm) and M.B.A (marketing).
His most recent success includes the successful launch of the medical tourism company, ARTbaby, which offers treatment options for infertility, egg donation, and surrogacy. He likes spending time with his family and writing about various aspects of IVF surrogacy and donating eggs.